Field Activities Tunisia
- Details
- Created on Monday, 01 October 2012 08:55
- Written by Erik van den Elsen
The following WHT were described with the WOCAT questionnaires
|
Country |
Technology |
Description |
Picture |
|
Tunisia |
Jessour |
Jessour are made of three components: the impluvium, the terrace and the dyke. Each unit has its own impluvium, but can also receive excess water from upstream units. Farming is practised on the terrace; which is formed progressively by the deposition of sediment behind a dyke |
 |
|
Tunisia |
Gabion check dam |
In order to slow down the water flow in the wadi courses and improve its infiltration into deeper soil layers and geologic formations, small check dams are installed on the wadi beds |
 |
|
Tunisia |
Tabia |
Tabias, like jessour, are comprised of a dyke, a spillway and an impluvium. The differences between the tabia and the jessour systems are that the former contains two additional lateral bunds (up to 30 m long) and sometimes a small flood diversion dyke |
 |
|
Tunisia |
Cistern |
Cisterns are reservoirs used for storing rainfall and runoff water for multiple purposes: drinking, animal watering and supplemental irrigation. |
 |
|
Tunisia |
Recharge well |
A recharge well is made of casting tube, drilled upto 30-40 m to reach the water table, and a filter used to allow the direct injection of floodwater into the aquifer |
 |
The following WHT were selected for test-implementation
- Jessour
- Gabion check dam
- Tabia
- Cistern
- Recharge well
Picture below gives an impression of the workshop in which the selection was made.

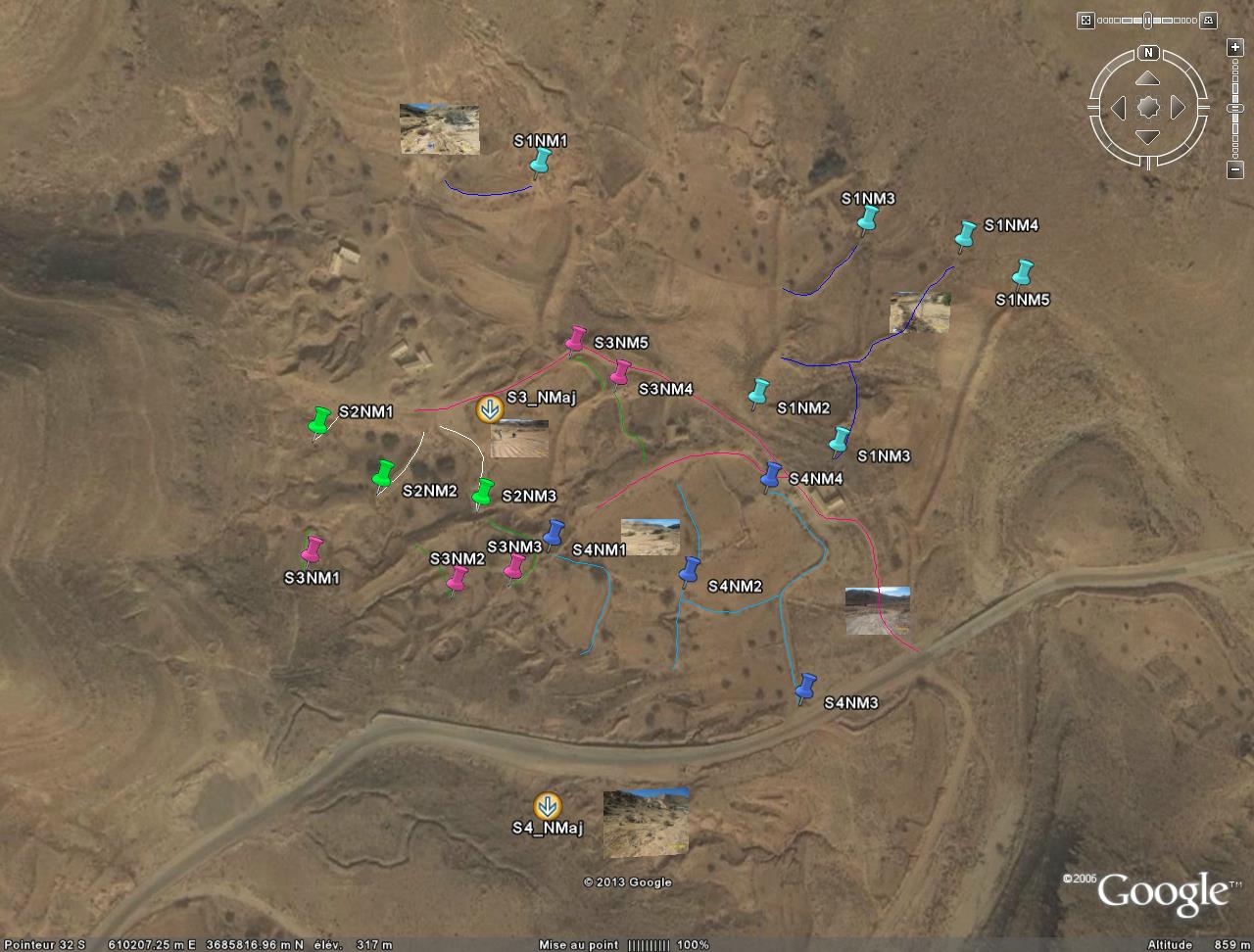
| A site for field implementation was selected, and WHT were implemented for testing. Monitoring is currently on-going. The figure below shows the monitoring locations. |